
Introduction to Business
1) Define business. Explain its features ?
Business is derived from the English word “bisig” literally means a state of being “busy”. It is a part of social system. Every action taken in a business is related to the external world around it. Every individual in a society is related to the business activity. It is a
gainful human activity. It is concerned with creation, exchange and possession of wealth.
According to B.O. Wheelar, “Business is an institution organised and operated to provide goods and services to society under the incentive of private gain.”
The main important features of business are as follow:
1) Economic activity : Business is a form of an economic activity. It is the fruitful occupation for millions of people around the world like traders, bankers, industrialists, manufacturers and many more including professionals and those employed.
2) Regularity in dealing : Business activity is carried out regularly. It is not merely sale or exchange but the regularity or continuity of such dealings that constitutes business. A single transaction does not constitute business. The production or exchange of goods or services for a price is undertaken regularly and continuously in business.
3) Profit motives : Business is an income oriented activity. Every businessman expects profit from the transactions. The main object of business is to earn profit. Businessman earns profit from the business transactions and the buyer satisfies his wants of goods and services.
4) Organized activity : Business is an organised activity concerned with production and distribution of goods and services. A firm must conduct consumer research to identify consumer needs and wants. There is a constant need to monitor customer needs and wants, and accordingly produce and distribute goods and Service. Business has to be conducted systematically with continuous research and development. It should be organized in a systematic manner so that business objectives can be achieved successfully.
5) Degree of scale : Business can be undertaken at varied degree of seals of operation. Some firm like Sole trading concerns may undertake business on a small scale and that too in a local area. However, some firms, like joint stock companies may undertake business on a large scale, even at a global level.
6) Risk and Uncertainties : Business activities are always risky and uncertain. A business is likely to suffer huge loss due to a number of possible reasons such as change in fashion, tastes, preferences, government policies, technology, recession in the economy, natural calamities etc. All business risks can’t be insured. A business, however, can minimise risks through proper foresight and planning.
7) Societal Interest : At present, business firms place emphasis on “societal concept” of business. Business make efforts to preserve and promote customers’ and society’s well-being. Business unit try to achieve a balance between profit + Consumer satisfaction + public Interest. Therefore, increasing efforts are made to produce eco-friendly products to satisfy consumer.
8) Social Responsibility : Professional business firms are conscious of their social responsibility. The firm try to fulfill their social responsibility towards various groups. It needs the support of the groups i.e. investers, employees, consumers, creditors and so on. It can’t function without an active participation from these social groups. This feature of business in getting more importance in today’s era of a globalization.
9) Customer Satisfaction : Modern business world is a consumer oriented. Customer is the King and Centre of all marketing activities. Professional business firms adopt customer oriented approach in their business operations. Business firms give importance not only to profit earning but also to customer satisfaction. Customers would be satisfied only when they get real value for their purchases. Business firms have to take care of not only customer satisfaction but also have to delight the customers by providing better and additional services.
10) Creative : Modern business is creative in nature. These days, consumers can’t be satisfied with the same type of goods and services. Hence business organizations have to be innovative or constantly search new ideas and proposals.
11) Dynamic : Business is a dynamic activity. There is a certainty of change in business Dynamic forces are at work from day to day. Within
business new products, methods, innovations in management cause ever changing adjustment of policies and administration. From outside forces such as government regulation, war, changing consumer income and new development in science and an art.
12) Government Control : Business organizations are subject to government control. The government of each country enacts laws and regulations to control and regulate business activities. Business organisations are expected to adhere to such laws.
13) Buying and Selling : All business activities are directly or indirectly connected with transfers or buying and selling of goods and services. Business is useful to buyers and sellers. Businessmen as Seller of goods and services, provide convenience and satisfaction to buyers through provision of form utility, place utility and time utility. In return for the supply of utilities, businessmen receive profit benefit from the buyers.
2) Explain the functions of a business
Functions refer to series of activities or tasks performed to achieve pre determined objectives. For the smooth conduct of business activities, there is a need to perform certain important functions. These functions are as follows.
1) Purchase and store keeping: Business firms have to make a series of purchases for conducting business activities. Such purchases include the buying of raw materials, components, spare parts, movable and immovable, assets relating to the functioning of the business activity. Traders purchase finished goods in order to sell these.An allied function would be to store the raw materials purchased for which a separate and special facility has to be provided.
Care must be taken to maintain proper inventory of materials. Over stocking of material block the working capital on the other hand, under-stocking blocks the production cycle. Further, there must be a proper stock of finished goods so as to distribute them as per the delivery schedules.
2) Production: Production means conversion of raw material in to semi finished or finished product. The production department deals with activities like design of the operations system (product design, process design, and location of facilities, facilities layout and capacity planning) and operation and control decisions (routing, loading, scheduling, dispatching and expediting).
3) Marketing Function: This function is concerned with, Controlling the level and composition of demand. If deals with creating and maintaining demand for goods and services produced by the production department. It determines physical attributes of the product, fixes its price, motivates consumers to buy the same through advertisement, personal selling and Sales promotion and determines the path through which goods will be transferred from sellers to buyers.
4) Finance Function: This function deals with obtaining and effectively utilising funds necessary for efficient Operations. It ensures that right amount of finance, at right cost and at right time is available for carrying out business Operations. It also deals with investment of funds in long-term assets and short-term assets to ensure smooth business functioning.
5) Personnel Function: This function deals with effective utilisation of human resource. It aims at selecting right persons at the right place
i.e. jobs and motivating them to work through team work and co- operate to achieve organizational goal. They have to do the work with commitment and loyalty.
6) Research and Development: Research and Development plays an important role in product development. It helps to bring out product modifications and product innovations. Business firms need to spend a good amount of time on research and development activities. Many professional business firms set up a separate department for research and development activities to make change in the business as per the requirement.
7) Public Relations: There is a need to maintain good public relations with the various sections of the public. Therefore, it makes a good sense to maintain separate department to look after public relations, especially in the case of large firms. It handles public queries, media queries, interviews, complaints etc. It develops the good public relation and bring positive image in the minds of the customer about the business, firm.
8) Sales Function: The Sales department works in close co-ordination with the marketing department. The sales department is concerned with the Selling activities of the firm. It books orders from the customers and then distributes the goods through the distribution channels. This is one of the most important functions of business, through which satisfied the consumers needs and wants.
3) Explain briefly the scope of business ?
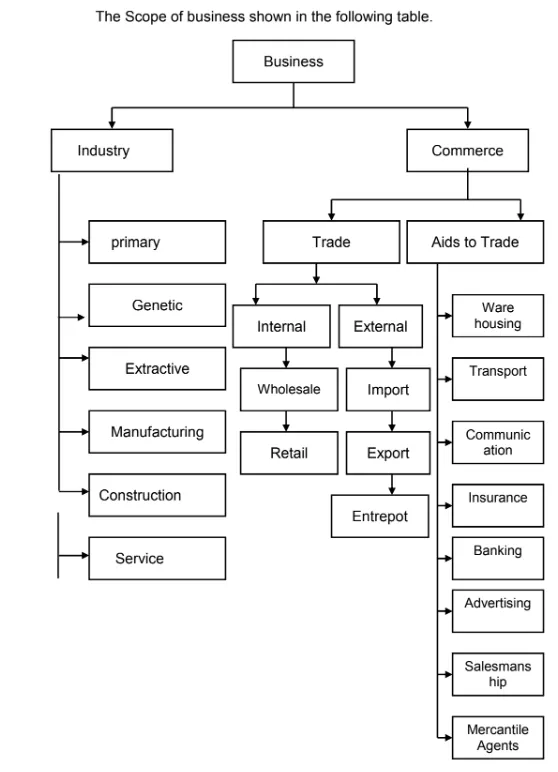
1) Industry : The term industry refers to that part of business activity which directly concerns itself with production, processing or fabrication of goods and services. It creates form utility. In industry, raw materials are converted in to finished products, which can be used for consumption. Some industries manufacture consumer goods while others manufacture capital goods.
Following are the various types of industries-
a) Primary Industries – These industries are engaged in the production of primary goods, such as rice, cotton, fish etc.
The best examples of this type of industries are Agriculture, fishing etc.
b) Genetic Industries – Genetic industry involves breeding and reproduction of plants and animals for the purpose of sale. Poultry, Plant nurseries, sericulture etc. are examples of genetic industry. The price of products available from such activities is generally less.
c) Extractive Industries – Extractive industries extract valuable minerals, ores etc. from the natural elements like soil, water and air. These industries are concerned with the discovery and utilisation of natural resources such as minerals and forests.
d) Manufacturing Industries – Manufacturing industries are concerned with the conversion of raw material into finished goods. They create form utility. The products of primary and extractive industries such as cotton, iron-ore, crude oil, etc. are used as a raw material in these industries.
e) Construction Industries – Construction industries are concerned with the construction work like construction of bridges, dams, canals, roads, harbours, building etc. These industries do not operate in factory buildings but at the site allotted.
f) Service Industries – Service industries produce intangible goods i.e. goods which can’t be seen or touches for example transport, insurance, banking etc. These services are essential and useful for the expansion of business.
2) Commerce : Commerce involves all those activities which facilitate transfer of ownership and movement of goods from the centers of production to the centers of consumption. In other word it involves all forms of trade and the services that assist trading. Commerce include trade and aids to trade.
A) Trade : Trade means buying and selling of goods and services. It involves transfer of ownership of goods from the seller to buyer
against money. In other words, trade is an exchange of goods and services for a price which the consumers are ready to pay. Consumers may be an individuals, government and industries who need raw materials.
1) Internal Trade : Internal trade is also known as home trade. It is conducted within the country. It can be at local level, regional level or national level.
a) Wholesale trade : It involves buying in large quantities from producers and selling in smaller lots to retailers. The wholesaler is a link between
manufacturers and retailers.
b) Retail Trade : Retail trade involves buying in smaller lots from the wholesaler’s and Selling in very small quantities to the consumers for personal consumption. The retailer is the last link in the chain of distribution. He established a link between wholesaler and Consumers.
2) External Trade : The trade carried on between the traders of two different countries is called external trade. It is also called as International trade or foreign trade. It includes following trade.
a) Export Trade : Export trade involves selling of goods from one country to another. For example, when goods are sold from India to America.
b) Import trade : Import trade involves buying of goods from a Seller of another country. For example, a buyer from India purchases goods from a seller of china.
c) Entrepot trade : When goods are imported from one country and then re- exported to some other country, it is called entrepot. For example an Indian trader may buy goods from Bangladesh and then sell it to Pakistan.
B) Aids-To-Trade : Aids to trade constitute another component of commerce. Aids to trade include various agencies which are useful for the
conduct of trading activities. There are as follows.
a) Warehousing : There is a time gap between production and consumption. However, goods which are produced at one time are not consumed at the same time. Hence, it becomes necessary to make arrangement for storage or warehousing. Agricultural commodity like wheat and rice are seasonal in nature but are consumed throughout the year. On the other hand goods such as Umbrellas and woolen cloths are produced throughout the year but are demanded only during particular seasons. Therefore goods need to be stored in warehouses till they are demanded.
b) Transport : There is a place gap from the place of production to the place of consumption. Goods are produced in one part of the country and Consumption in other parts of the nation. Transport fills the place gap. It meets out the gap between producer and consumer. It helps the manufacturer to expand their markets from local to regional, regional to national and national to global.
c) Communication : Communications facilitates transfer of information. It involves transfer of messages from one person to another and from one place to another. It can be in oral or writing form of information. Oral communication can take place through telephone or personally. Written communication is possible through letter, fax, e-mail etc. It facilitates quick transfer of messages to take important decisions quickly.
d) Insurance : Insurance reduces the problem of risks. Business is subject to risks and uncertainties. These are inevitable in the field of business. Risks may be due to fire, theft, accident or any other natural calamity. Insurance companies who act as risk bearer cover risks. Insurance tries to reduce risks by spreading them out over a greater number of people. The rate of premium depends upon the type of risks and the period for which the risk is covered.
e) Banking : Banking solves the problem of payment and facilitates exchange between buyers and sellers. Lending and borrowing the funds are the traditional functions of the banks. Banks provide short, medium and long term loans to the needy people. Other functions have started gaining importance such as merchant banking, development banking, credit cards etc. This has further facilitated to trade.
f) Advertising : Advertising as a powerful marketing tool of communication is highly useful to the manufacturer, retailers, consumers and the
society at large. Advertising is basically designed to inform, create interest and induce people to act in a particular way. It can be used for communicating both commercial and non-commercial messages. It creates awareness of the product and builds a good brand image in the minds of consumer and society at large.
g) Salesmanship : Salesmanship refers to personal presentations by the firm’s sales force for the purpose of making sales and building customer relationships. It facilitates personal selling. The salesmen provide information to the buyers. They convince and persuade buyers to buy goods.
h) Mercantile Agents : In the process of distribution, producers and consumers are unable to have direct contact, as consumers are spread over a vast area; mercantile agents remove this difficulty of personal contact. Mercantile agents are the intermediaries who form a link between the buyers and the sellers. They do not carry business in their own name. These are several types of mercantile agents such as brokers, commission agents, auctioneers, underwriters, insurers, etc.
4) Discuss the significance of business to the firm ?
Answer : Business is useful to the society in general and the business firms and consumers in particular as it create utilities. Let us see the benefits it offers to various groups. Following are the significance of business to business firms.
a) Accomplishment of objectives : Business helps the firms to achieve its various objectives. It creates utility by creating goods and services. These goods and services are consumed by the people for the satisfaction of needs and wants. Thus with increased sales firms can achieve the objectives, like increase in sales, increase in profit etc. Besides earning profits firms are able to achieve its other objectives such as increase in market share, growth and expansion, creating goodwill etc.
b) Improvement of knowledge and skill : Managing business, interacting with people, trying to develop new methods and techniques etc. It helps in improving the knowledge and skills of the employer and employees involved in business. This ultimately benefits to the business organisation as the overall functioning of the business firm improves.
c) Expansion of business : Healthy and sound business practices help the organisation to grow and expand its activities. Firm can introduce new and better products in the market and can expand its activities. Firm can also expand its area of market operations. Market expansion can be right from local to international level.
d) Product Development : Business undertakes marketing research and product research activities regularly for the purpose of product development. Due to these research and development activities, firms are able to introduce new, innovative and better products in the market. Thus advanced products benefit to the consumers as well as business firms.
e) Improve Relations : Sound business practices improve relations of a firm with various sections of the society. Business firms need to maintain
good relations with dealers, suppliers, customers, government authorities, media people, and society in general. The survival and success of business is depends upon the business relations with the stakeholders.
f) Corporate Image : Business helps the organisation to create and improve corporate image in the market. Business can create a good reputation about itself in the minds of employees, shareholders, investors, consumers, government and general public. Corporate image is vital to any organisation, as it enhances marketing, financial and social value of a firm. Corporate image helps the forms for long term Survival.
g) Optimum Utilisation of Resources : Resources are the basic inputs which are necessary to produce goods and services. The resources are limited and in short supply. Hence, it should be used in such a way that it will ensure minimum use and maximum output. In achieving its goals business ensures optimum use of scarce resources by utilising it in most profitable areas. Sound business practices enable a firm to make optimum use of resources.
h) Increase in market Share : Every organisation desire of increasing its share in the market. Increase in market share brings in more profits, more respect, better image and increase in market value of shares. Sound business practices enable a firm to increase in market share and create more goodwill in the market.
i) Increase in profit : Every business is subject to risk and uncertainties. Profit is the reward for their risks undertaken by the businessman with the help of business activities a business firm able to earn profits. Profits play a role of return on the investment done by businessman.
5) What are the significance of business to the customer ?
Answer : Business plays a significant role in respect of consumer. Following are the significance of business to consumers.
a) Better quality of goods and services : Now a days, competition has increased tremendously. To face this competition, firms try to make every possible effort to improve the quality of goods and services. Business firms make available quality goods and services required by consumers.
Business provides better quality of goods and services to the prospective buyers.
b) Reasonable price : Today’s market is a consumers’ market where supply exceeds demand for products. In order to attract consumers, business firms offer quality goods and services at competitive prices. They try to offer value for money. Business provides goods and services at right prices.
c) Better facilities and Services : Every business wants to survive in the competitive business world. It tries to provide better facilities and services to the customers at low cost. The services like after sale-service, free home delivery, extended warranties, Sale on installment basis, zero rate of Interest etc. are provided by the business firms. Due to these facilities and services customers are benefited to a great extent.
d) Customer Satisfaction : Modern business has become consumer oriented. Moreover, in order to survive and grow, business organisations thrive to provide consumer satisfaction. Their objective is to retain the old customers as well as to find new customer. Some professional
business firms go a step forward to delight its customers by providing additional facilities.
e) Higher Standard of Living : Business generate employment in areas of production, distribution, banking, transport and so on. This increases the level of income and create additional demand for product in the market. This in how business generate demand which in turn result in more jobs and income which finally result in satisfying the number of human wands and increase their standard of living.
6) Explain the Significance of business to the society ?
Answer : Business plays a significance role towards the society. Following are the significance of business to the society.
a) Economic Growth : Business activities facilitate economic growth in the country. It undertakes expansion and diversification activities. New products and services are offered to consumers constantly. New business firms are set up thereby leading to accelerated rate of growth.
b) Regional Development : Business firms facilitate to bring about regional development. Government encourages business firms to start operations in under developed areas by giving tax benefits, duty concessions and so on. This leads to a balanced regional development.
c) Revenue to the Government : Business firms provide substantial revenue to the government. Business sector provides revenue through taxes, duties, customs duty, sales tax, corporate tax, Octroi etc. contribute to the income of the government. The government can also generate revenue by way of profits earned by public sector units.
d) Employment Opportunity : Business provides employment to number of people. It provides employment in the activities such as production, distribution, marketing, promotion of products, and so on. It is thus a source of employment to the people. A large section of the population of the world earns its regular income by means of business.
e) Social Welfare : Business helps in social welfare of the society. It can be in the form of starting schools and Colleges, providing donations for
starting hospitals, sponsoring various sports and cultural events and so on. In other words they undertake various social welfare programmes and there by reduce the burden of the government.
f) Capital Formation : Business facilitates capital formation in the country. Capital formation takes place as a result of savings and investment in the country. All those connected with business i.e. business firms, employees, traders, service providers and other save part of their income earned from business. These savings are put into investments. These investments lead to capital formation in the country.
g) Global Relations : Business helps to maintain good and cordial relations with other countries. This is because of foreign trade. Foreign trade enables countries to be dependent on each other, which in turn helps to develop good and friendly relations among participating countries. Sound business tries to build a cordial relation with other countries.
7) Distinguish between traditional and modern concept of business.
| Traditional Concept of business | Modern concept of business | |
| Meaning | As per the traditional concept, business means production and marketing of goods and services for private gain. | As per the modern concept, business means provision of goods and services for the satisfaction and welfare of consumers and the society at large. |
| Scope | The Scope of business was restricted to local market. | The scope of business covers national and even global market. |
| Objectives | The Objectives of business was profit. Business was treated as the end in itself. It was production and distribution for earning profit. | The Objectives of business is consumer satisfaction and service to society. Business is treated as a means to serve the society and rise social welfare. |
| Position of Consumer | Consumers were neglected and were taken for granted. They were exploited for profiteering. No attention was given to consumer welfare. | Consumers are given priority and business is adjusted as per the needs and expectations of consumers. Consumer welfare is given special attention. |
| Social Orientation | Social orientation to business was absent. | Business is treated as social institution with social obligation. |
| Social Responsibility | The concept of social responsibility was absent. Business was not socially responsible. | Business accepts and honors social responsibilities. It is treated as an integral part of social system. |
| Nature of concept | It is treated as old, outdated and narrow concept as business is treated merely as profit making activity. | It is treated as dynamic and broad concept as it is given social orientation. It is for the satisfaction of human wants. |
| Role of profit | Profit was the sole purpose in business. Profit alone was the guiding principle in business. | Profit is given secondary position. Profit through service is the guiding principle in business. |
| Traditional concept was businessman oriented i.e. profit oriented. Limited importance was given to consumers and social welfare. | Modern concept is social oriented i.e. consumer oriented. Special importance to consumer satisfaction and social welfare and not merely to profit making. |
You can download fybcom commerce 1 book pdf – Click here
Related Posts :
FYBCOM Subjects
SYBCOM Subjects
TYBCOM Subjects
FYBCOM Syllabus
SYBCOM Syllabus
TYBCOM Syllabus
FYBCOM books pdf
SYBCOM books pdf
TYBCOM Books Pdf
Pingback: New Trends In Business | FYBCOM Commerce Chapter 3 | Mumbai University - University Solutions
Pingback: FYBCOM Sem 1 Commerce Chapter 4 Notes | Business Environment | Mumbai University - University Solutions
Pingback: FYBCOM Sem 1 Commerce Chapter 5 Notes | International Environment | Mumbai University - University Solutions
Pingback: Explain the Objectives Of Business | FYBCOM Commerce Chapter 2 - University Solutions
Pingback: FYBCOM Sem 1 Commerce Chapter 6 Notes | Project Planning | Mumbai University - University Solutions
Pingback: FYBCOM Commerce Sem 1 Chapters 7 Notes | Business Unit Promotion | Mumbai University - University Solutions
Pingback: FYBCOM Commerce Sem 1 Chapter 8 Notes | Entrepreneurship | Mumbai University - University Solutions
Pingback: FYBCOM Commerce Sem 1 Chapter 9 Notes | FYBAF | FYBMS | Mumbai University - University Solutions